First, the definition and concept of power
Power is an important parameter that characterizes the electrical signal. It is defined as the rate at which energy is transferred between systems or between components within a system; a given component can either supply energy or energy or be absorbed by the component. The basic definition of power is described by the following relationship:
Power (P) = d (energy) ÷ dt, or: energy = ∫ (power) dt
Simply put, power is defined as the work done in a unit of time. The basic unit is watt (W), 1W is equal to 1 joule of work in 1 second. Commonly used power units are MW (1MW=106W), kW (1KW=103W), milliwatt (1mW=10-3W), microwatt (1μW=10-6W), and tile (1PW=10-12W) . Another commonly used power unit is expressed in decibel milliwatts (dBm): it takes 1 milliwatt as the reference level P0=1mW, and the actual power value P(mW) is compared with P0 and takes the logarithm, which is the absolute unit of power. That is, dBm=10lg(P/P0)=10lgP; decibel (dBW) can also be used as the power unit, at this time P0=1W, that is, 1dBW=10lg(P/P0)=10lg103=30dBm.
Power is also different in terms of definition and measurement depending on frequency. In general, in the DC and low frequency ranges, the power can be calculated by measuring the voltage and current. The instantaneous value of the power can be expressed by:
Instantaneous power = voltage × current, ie P(t) = u(t) x i(t).
The instantaneous power is constant when DC; the AC signal is measured by the average power, that is, the rate of change of the net energy that occurs in one cycle of the signal, that is, for the periodic signal with period T, the average value of the instantaneous power in one cycle is called active power. . The relationship between average power and instantaneous power is as follows:
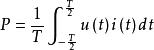
If the voltage and current are continuous (CW) sine waves, P = VIcos∮, where V and I are effective values, ∮ is the phase angle between voltage and current; for non-sinusoidal circuits, assume U and I are AC power n times The effective value of the harmonic component, ∮ is the phase difference between the nth harmonic component of the voltage and the nth harmonic component of the current, P is the active power of the nth harmonic component, and the above formula is still true; when n=1, P is The fundamental power is active. If the voltage and current are discontinuous (CW), it is generally expressed in terms of pulse peak (PW) power.
There are TEM waves and non-TEM waves in the UHF and microwave bands. In a coaxial system of TEM waves, although the voltage and current have exact meanings, it is difficult to measure the absolute value. In waveguide systems, voltage and current lose their uniqueness because of the different electromagnetic modes. In a single frequency band and in each transmission system, power is an important method for characterizing the signal strength in a single value.
Second, the measurement of power
The instrument for measuring power is a power meter or a power meter. The power meter can be divided into three according to the measurement frequency range (low frequency 20Hz-200Hz, intermediate frequency 200Hz-6000Hz, high frequency 6KHz-20KHz, radio frequency 20KHz-1GHz, radio frequency 1GHz or higher, light wave). Direction: 1. Electric power meter for DC and low frequency signal measurement; 2. High frequency power meter for RF or microwave signal measurement; 3. Optical power meter. According to the specific frequency of the signal to be tested, the power meter can be divided into: a DC power meter, a power frequency power meter, a frequency conversion power meter, a radio frequency power meter, a microwave power meter, and an optical power meter.
Generally speaking, electric power meters are commonly used; electric power meters are also called watt meters, an instrument for measuring electric power. Electrical power includes active power, reactive power, and apparent power. When not specified, the power meter generally refers to the meter that measures the active power. Since the DC power is equal to the simple product of voltage and current, in actual measurement, voltmeter and ammeter are generally used instead. The power frequency power meter is a commonly used power meter. The power meter is generally referred to as a power frequency power meter. The variable frequency power meter is the product of the rapid development of the 21st century frequency conversion speed control technology. (For details on the electric power meter, please refer to the article "Introduction to Electric Power Meter Measurement")
The RF power meter and the microwave power meter directly measure the power in the RF range instead of the voltage and current. The high frequency power meter generally consists of a power sensor and a power indicator. The power sensor, also called the power meter probe, converts the high-frequency electrical signal into energy that can be directly detected by the energy; the power indicator includes the signal amplification, conversion, and display, and the display directly displays the power value. (For details on the high-frequency power meter, please refer to the article "Introduction to RF Power Meter Measurement")
An optical power meter is used to measure absolute optical power or relative loss of optical power through a length of fiber. In fiber optic systems, measuring optical power is the most basic measurement, much like a multimeter in electronics. By measuring the absolute power of the transmitter or optical network, an optical power meter can evaluate the performance of the optical equipment. Using an optical power meter in combination with a stable source, it is possible to measure connection loss, verify continuity, and help evaluate fiber link transmission quality. (For details on the optical power meter, please refer to the article "Introduction to Optical Power Meter Measurement")
According to the transmission and absorption of energy, the power meter is also divided into: 1. Transmission type power measurement, commonly known as pass-through power meter, common household electric meter; 2. Absorption power measurement, commonly known as terminal power meter, common is Terminal load.
The power meter core is selected to consider the following five indicators: measurement power range, meter accuracy, frequency range, stability, and test methods. Please contact Marine Instruments 010-62178811 for discussion of this article.
Leather Bar Chair is made of leather, can be available with italian leather, aniline leather and some synthetic leather. Now more customers prefer leather bar chair, cause it is soft and comfortable for seat, the leg is usually made of stainless steel and solid wood. We have produced some high quality bar chairs, like LEM leather bar chair, four seasons bar chair, some customers like these designs, if you are also interested in the leather bar chair, you can also contact us for further information.
Leather Bar Chair,Full Leather Bar Chair,Aniline Leather Bar Chair,Leather Kitchen Bar High Chair
DELO SOFA , https://www.modernluxuryfurnitures.com