As the Internet occupies an increasingly important position in e-commerce and human life, people's requirements for authentication and secure transactions are getting higher and higher. The smart card has the advantages of small size, light and easy to carry, can store and process data by itself and can perform encryption and decryption operations, and combines with network services, making it a device that can conveniently store user keys and download confidential data. The smart card contains CPU, RAM, EEPROM, ROM and I/O, just like a smaller computer. The software structure of the smart card is composed of a COS (Chip Operating System) system, a smart card application framework, and a specific application program, as shown in FIG. In this structure, the lowest-level COS system is responsible for the management of the underlying hardware; the smart card application framework defines a set of programming interface classes that provide the unified application environment required by the application; the application provides specific smart card services.
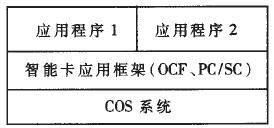
Figure 1 smart card software structure
1OCF and PC/SC Overview
PC /SC (Personal Computer / Smart Card) is a standard framework for smart card access on the Windows platform. Its purpose is to ease the development of smart card applications on PCs. The main advantage of PC/SC is that the application communicates with the smart card without having to consider the specific details of the smart card reader. As long as the smart card reader complies with the PC/SC standard, the application can function normally through the smart card reader. The PC/SC architecture is shown in Figure 2. Among them, the smart card is the Integrated Circuit Card, and the smart card reader is Tnterface Devices. After the smart card is inserted into the reader, the smart card reader communicates with the driver's smart card read/write controller (IFD Handler). The ICC Resource Manager manages a variety of smart card reader and smart card resources. Each smart card reader communicates with the smart card resource manager through its own smart card read/write controller interface function. The smart card resource manager sends the commands sent by the upper layer software to the corresponding smart card according to the requirements of the upper layer software. The controller then sends it to the smart card reader and smart card.
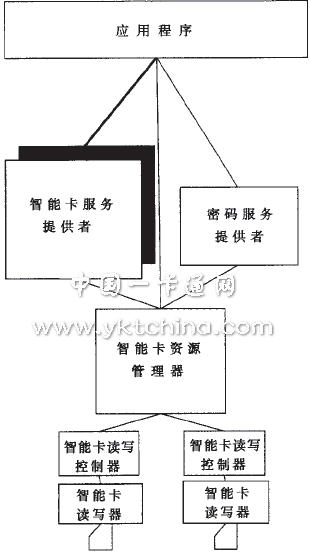
Figure 2 PC/SC architecture
OCF (Open Card Framework) is an easy-to-use standard framework for implementing smart card solutions and smart card services. OCF leverages Java's cross-platform, multi-purpose features to provide an open architecture and a set of common applications (APIs) for smart card solutions and smart card services. The architecture of OCF is shown in Figure 3. Among them, the smart card service (Cardservice) is an abstract class, the meaning of which is the service on the card. Its subclass provides specific service content by packaging a series of APDUs (Application Protocol Data Units); the smart card service identifier (Card Serves Factory) The functions of the Card Terminal Factory are similar. The application service provider provides its own smart card service identifier to represent itself. The smart card service identifier generates various services, that is, some smart card service instances; smart card service management (Card service registry) management. All smart card service objects on the card; the Card servces shcduler provides a logical channel for the communication required by the service, and provides a logical channel for the smart card service object to send and receive commands to complete the task; the smart card terminal (Card Terminal) The smart card terminal abstracts the class that can be inherited, which is produced by its corresponding Card Terminal Factory; the smart terminal terminal management (Card Terminal Registry) manages all the smart card terminals installed in the application system, and can execute the example of the smart card terminal. Registration, logout, etc.; smart card terminal identification is the same as that produced by a specific factory. Different smart card terminal manufacturers provide specific smart card terminal identification subclasses, and these subclasses generate corresponding smart card terminal instances.
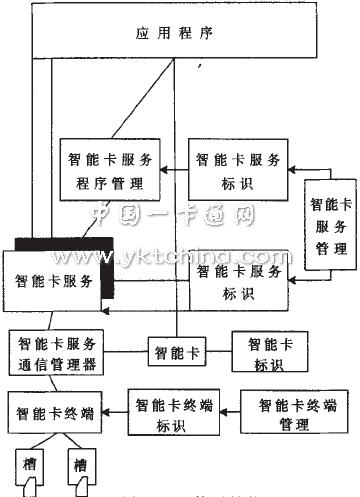
Figure 3 OCF architecture
2 OCF and PC/SC contact
Both OCF and PC/SC provide access standards for smart cards and various computers, and they have something in common in terms of concepts and mechanisms. By comparing their composition, the commonalities and differences between them can be found.
(1) The commonality between OCF and PC/SC structure
The smart card service provider in the PC/SC provides the smart card service, which is provided by the smart card service in the corresponding OCF; the smart card terminal in the OCF corresponds to the smart card reader system in the PC/SC (Inte 5). Therefore, OCF has much in common with PC/SC. Specifically, as shown in Figure 4.
Full text download: http://Read-b3-t4213-p1.htm
This phototherapy lamp is a kind of health auxiliary lamp, and its light is a healthy light without ultraviolet rays and regulated uniform light and simulating sunlight. You can use it at a certain distance from the side to light up, use it to fill in the light, relax your mood, and relieve stress. For example: while working on a desktop, reading a book, looking at a computer or doing yoga.
In high-latitude countries in Europe and America, winter is usually shorter, and people need supplemental light to enrich themselves. It can eliminate the discomfort symptoms such as dizziness, insomnia, and inability to concentrate in winter. And those who often need to travel by air to eliminate jet lag.
Typical usage time is 1-2 hours, you can adjust the color temperature and brightness to your comfort. Or start the product timed shutdown function. The compact and convenient body allows you to take it to your home or office.
Rectangle Light Therapy Lamp,Light Therapy Lamp,Portable Sad Light Therapy Lamp
Guangdong Jishengke Industrial Co.,Ltd , https://www.jskpad.com